4 Types of Long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs): How Is It Efficacy Rate?


Long-acting reversible contraceptives, or LARCs, offer women a reliable form of contraception that doesn't require daily administration, making them particularly appealing for long-term, effective birth control. "LARCs are highly effective methods of birth control because they don't require a daily routine and leave less room for error" explains Dr. Karen Martin. It is crucial, however, to understand their differing efficacy rates in order to choose the most suitable one.
In this article, we will delve into four primary types of LARCs, each with its own set of advantages and efficacy rates: Intrauterine Devices (IUDs), implants, injections, and hormonal IUDs. Our objective is to provide a comprehensive guide that will facilitate an informed decision on the best contraceptive method for each individual.
Contraceptive efficacy refers to the effectiveness of a contraceptive method in preventing pregnancy. It is typically expressed as a percentage, with a higher percentage indicating a lower chance of pregnancy.
Several factors can affect contraceptive efficacy, including correct usage, individual health factors, and age. For instance, a 2021 study in the Journal of Women's Health found that correct and consistent usage of a contraceptive method significantly affects its efficacy.
"The importance of understanding contraceptive efficacy cannot be overstated," asserts Dr. Peter Thompson, a leading gynaecologist in the UK. "This knowledge helps individuals make informed decisions about which method is most suitable for them"

An Intrauterine Device (IUD) is a small, T-shaped device that is placed in the uterus by a healthcare provider to prevent pregnancy.
IUDs are available in two primary types: Copper T IUDs, which release copper to stop sperm from reaching the egg, and hormonal IUDs, which release progestin, a hormone that prevents ovulation.
The Copper IUD works by releasing copper into the uterus, which is toxic to sperm, inhibiting their ability to move and reach the egg. On the other hand, the hormonal IUD releases progestin, which thickens the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg and thins the uterine lining to prevent implantation if fertilization does occur.
Both types of IUDs have high efficacy rates. Copper IUDs have a success rate of 99.2% according to the National Health Service (NHS), and hormonal IUDs have a success rate of over 99% as reported by the British Pregnancy Advisory Service (BPAS).
IUDs offer several advantages, including long-term, reliable contraception and the ability to be removed at any time. However, they may also cause side effects such as irregular bleeding, cramps, and in rare cases, infection or uterine perforation. It's important to discuss these potential risks and benefits with a healthcare professional when considering this contraceptive option.
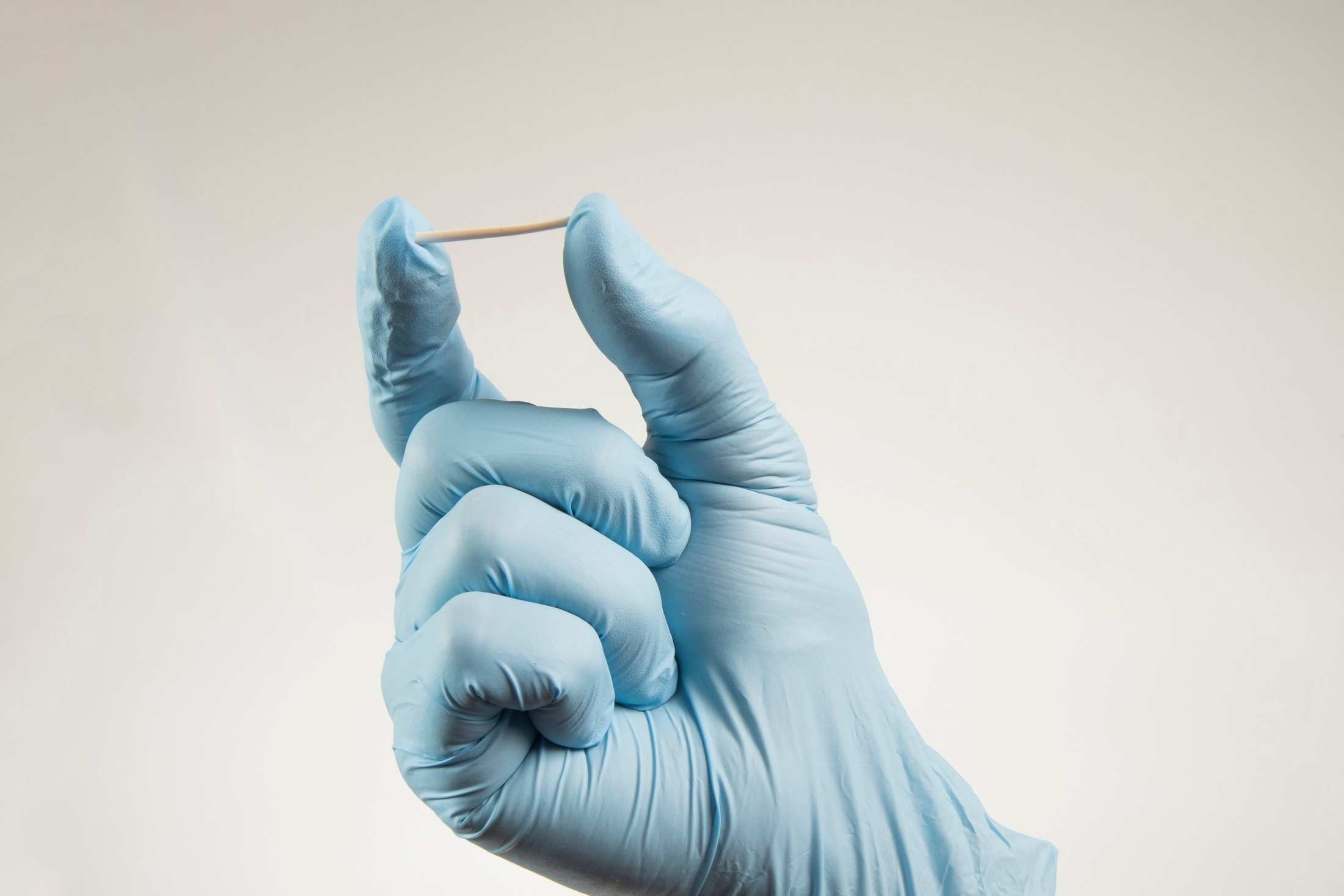
Contraceptive implants are small, flexible rods about the size of a matchstick that are inserted under the skin of the upper arm. "Implants release a progestin hormone called etonogestrel into the bloodstream to prevent pregnancy", as described by Dr. Alison Wright.
Contraceptive implants work by releasing a continuous low dose of the hormone progestin into the body. This hormone prevents ovulation (the release of eggs from the ovaries) and thickens the mucus in the cervix, making it hard for sperm to enter the uterus and reach any eggs that may have been released.
The efficacy rate of implants is over 99% with typical use, as reported by the NHS. This makes implants one of the most effective forms of contraception available.
Implants have several advantages including long-lasting effects (up to 3 years), convenience, and high efficacy. However, they can also have side effects such as changes in menstrual patterns, mood changes, and weight gain. "Like all contraceptives, the benefits and potential side effects should be discussed with a healthcare provider", notes Dr. Wright.
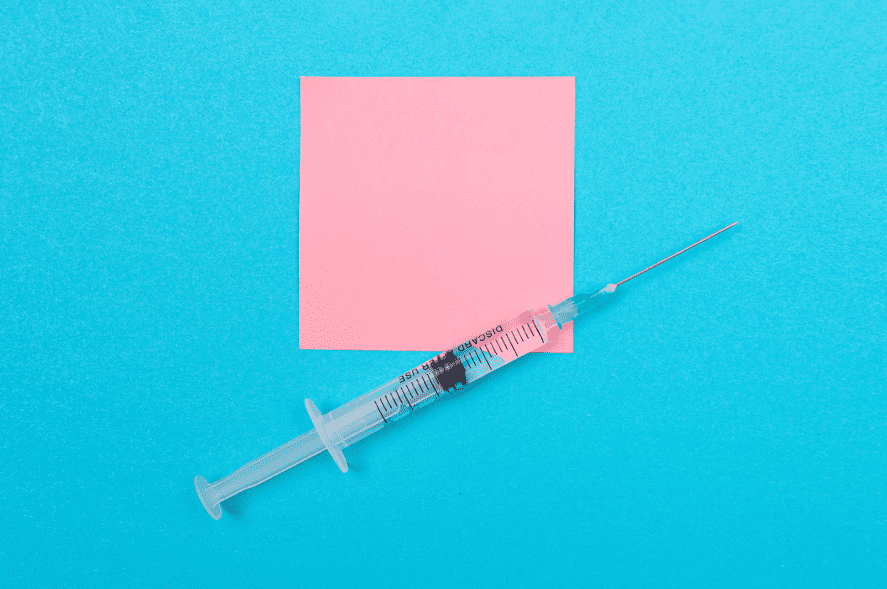
Contraceptive injections, also known as the birth control shot or Depo-Provera, involve the injection of the hormone progestin into the body every 3 months. This method is known for its convenience and long-lasting protection against pregnancy.
The injection works by slowly releasing the hormone progestin into the body. This hormone inhibits ovulation and thickens the cervical mucus, blocking sperm from reaching the egg. It also thins the lining of the uterus, making it less likely for a fertilized egg to attach and grow.
The efficacy rate of contraceptive injections is around 94% with typical use, as noted by the NHS. However, with perfect use, this rate increases to over 99%.
Injections offer the convenience of needing to be administered only every three months. Potential side effects include changes in menstrual bleeding, weight gain, and delayed return of fertility. Potential side effects should be discussed with a healthcare provider, advises Dr. Sarah Marsh.
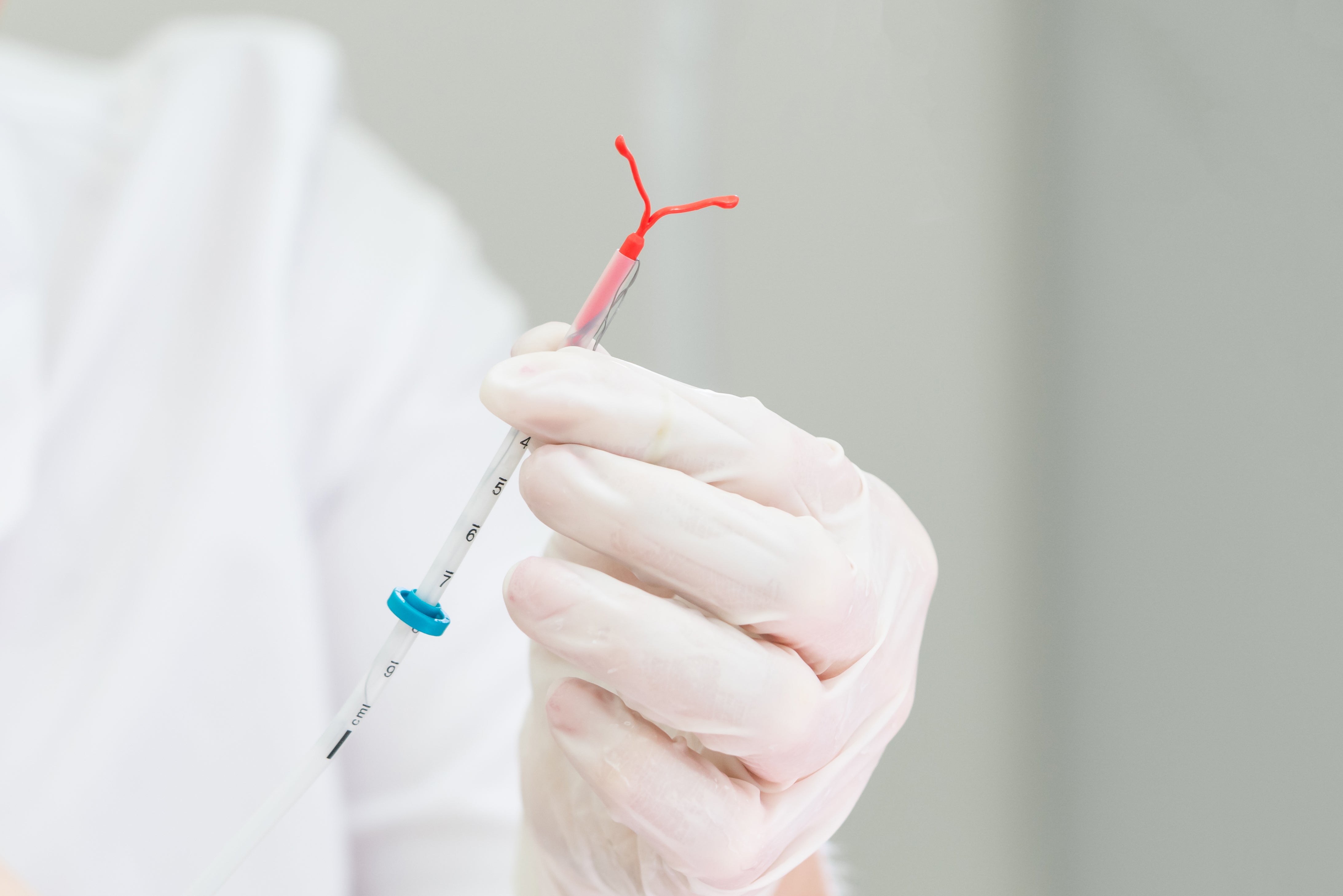
While both types of IUDs are inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy, their mechanisms of action differ. Copper IUDs work primarily by releasing copper, which is toxic to sperm. In contrast, hormonal I UDs release a form of the hormone progestin, which has multiple effects that prevent pregnancy.
Hormonal IUDs release progestin into the uterus. This hormone thickens the cervical mucus, preventing sperm from reaching the egg. It also thins the lining of the uterus, making it less likely for a fertilized egg to attach.
Hormonal IUDs are over 99% effective at preventing pregnancy, according to BPAS. This makes them one of the most reliable methods of contraception available.
Hormonal IUDs offer long-lasting contraception (up to 5 years) and can have the added benefit of reducing menstrual pain and heavy bleeding. However, they can cause side effects such as irregular bleeding, ovarian cysts, and hormonal side effects like mood changes. As always, these potential benefits and risks should be discussed with a healthcare provider when considering this contraceptive option.
| Type | Efficacy Rate |
|---|---|
| Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) | 99.2% (Copper T IUD), >99% (Hormonal IUD) |
| Implants | >99% |
| Injections | 94% (typical use), >99% (perfect use) |
| Hormonal IUDs | >99% |
While all LARCs have high efficacy rates, they vary in terms of usage, side effects, and personal preference. IUDs, for example, offer long-lasting contraception but may cause irregular bleeding. Implants provide similar benefits but can lead to weight gain and mood changes. Injections require administration every three months and can cause weight gain. Hormonal IUDs can reduce menstrual pain but may lead to hormonal side effects. It's crucial to weigh these factors when making a decision about contraception.
Efficacy rates are a key factor in choosing a contraceptive method. "A higher efficacy rate means less worry about unplanned pregnancy, which can be a huge relief for many women," says Dr. Laura O'Connell, a leading authority on contraception in the UK.
Besides efficacy rates, other factors such as personal health, lifestyle, cost, and personal preference are also important in decision-making. For example, some methods might not be suitable for women with certain health conditions, while others may not be affordable or accessible to all.
When choosing a contraceptive method, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalised advice based on your health history and lifestyle, ensuring you choose the method that is most suitable for you.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of Long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) and their efficacy rates can help inform your decision about contraception. With several highly effective options available, it's possible to find a method that fits your lifestyle and needs.
We hope this article has been informative in providing a thorough understanding of the four main types of LARCs: Intrauterine Devices (IUDs), implants, injections, and hormonal IUDs. Remember, while this article provides a comprehensive overview, personal research and consultation with healthcare professionals are key to making an informed decision about your contraceptive method.
Plus get the inside scoop on our latest content and updates in our monthly newsletter.