What are vitamin D tablets?


Everything you need to know about functions, deficiency symptoms, dietary sources and supplementation of vitamin D.

Vitamins are the organic compounds needed by the body in very small quantities. Nevertheless, they are vital for various physiological functions, and their deficiencies cause multiple problems. The body needs a lot of vitamins which fall into two categories, e.g., fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and water-soluble vitamins (vitamin C and B complex vitamins).
Each vitamin has its own functions and deficiency symptoms.
Vitamin D tablets are dietary supplements containing vitamin D. First; you need to know the different forms of vitamin D and why you need vitamin D.
Vitamin D is a major fat-soluble vitamin. It is found naturally in two forms, D2 and D3. The D2 (ergocalciferol) is of plant origin, while the D3 (Cholecalciferol) is of the animal origin. There is, however, practically no difference between the two types except that D3 is more potent in raising serum vitamin D levels and is present in most supplements, while D2 is cheaper and is present in most fortified foods.
Vitamin D is different from other vitamins. It is a fat-soluble vitamin as well as a hormone. It's an important hormone and has a role in the;
Absorption and retention of phosphorus and calcium, the two critical ingredients for bones and teeth
Regulation of inflammatory responses
Control of infections and
Suppression of the growth of cancer cells etc.
Besides these, the receptors of vitamin D are present in many different tissues and organs of the body, suggesting that it may have many more functions, and the scientific community is investigating its roles. Due to these reasons, the doctors may prescribe vitamin D tablets to you. But, before using these tablets, you need to have some basic know-how of vitamin D.

Why is vitamin D important? What are the most common symptoms of vitamin D deficiency? What are the possible risks and side effects of vitamin D tablets? Let's go through these topics one by one.
Vitamin D has various important functions in the body, and low vitamin D levels can cause multiple problems. Some important functions of vitamin D are;
The immune system protects you from infections by fighting the invading germs. However, an unregulated immune response can cause more problems than benefits. It happens when the immune system's identification mechanisms fail and begin to identify the normal cells of the body as foreign agents. Here vitamin D comes to your rescue as it regulates the immune responses, protecting you from the self-damaging aspects of immune response (autoimmunity).
Its receptors are present in the cells of the immune system, e.g., antigen-presenting cells, B cells, and T cells, and it modulates both the adaptive and innate immune responses. The research has found a link between vitamin D deficiency and autoimmune diseases, e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, diabetes etc. Vitamin D deficiency is linked to more risk of autoimmunity and infections. However, more research is needed on the topic.
Although the results of test tube studies are highly promising, controlled trials on humans are needed to confirm these findings.
You might take many calcium supplements but still have weak bones, teeth, and have symptoms of vitamin D deficiency. Where is the problem? The body absorbs some calcium and removes the remaining through faeces. The absorption of calcium can be even lower in the case of some infections. Here is the role of vitamin D. It improves the absorption of phosphorus and calcium from your intestines and thus improves bone mineralization.
The consequences of vitamin D and calcium deficiency can be devastating as it causes conditions, e.g.,
In children: The deficiency causes rickets, resulting in tooth issues and bone softening, leading to a bowlegged appearance.
In adults, two issues can occur;
Osteoporosis is the demineralization and weakness due to a long-term vitamin D deficiency. However, it is a complex issue, and several factors, e.g., age, menopause etc., can be responsible.
Osteomalacia is the immediate effect of vitamin D deficiency and causes muscle weakness and bone softening.
Vitamin D also seems to link with obesity as the research has shown that obese people tend to have more chances of vitamin D deficiency. It was reported in a review published in the Current Obesity Reports (a journal) that there is an inverse relationship between serum levels of vitamin D and body weight.
So, vitamin D supplements can aid in weight loss. Vitamin D alone doesn't help in weight loss. However, it has some relationship.
Vitamin D has some role in regulating mood, as research has shown that vitamin D supplementation decreases the risk and occurrence of depression.
For example, a 2019 study published in the Journal of Postgraduate Medicine found that the oral and parenteral supplementation of vitamin D has a favourable impact on depression ratings in patients with major depression. The study involved a total of 948 participants. The effect size was, however, moderate.
The role of vitamin D in disease prevention is also well known as it reduces the occurrence of heart disease, multiple sclerosis, respiratory distress syndrome, autoimmune diseases etc.
A randomized controlled trial study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition in May 2022 found that vitamin D supplementation at the rate of 1600-3200 IU per day caused some decrease in adverse cardiovascular events and invasive cancers. However, this effect was not statistically significant.

Similarly, another randomized controlled trial study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2019 noted that the supplementation did reduce the risk of invasive cancers and cardiovascular diseases, but the effects were not different from the placebo group.
Vitamin D is naturally produced in the skin cells under sunlight. Its deficiencies are rare in people who have adequate exposure to sunlight. However, inadequate exposure to sunlight due to any cause can cause vitamin D deficiency. The risk factors are;
You have darker skin. The darker skin colour is due to the presence of melanin in the skin cells. More melanin in the cells reduces their ability to prepare vitamin D under sunlight.
Living in an area where there is little to no sunlight
You are spending too much time indoors
You are living in an area having too much pollution that blocks sunlight
You regularly use sunscreen
You are malnourished.
Your kidney or liver is out of order as these organs are involved in vitamin D metabolism
You have some cancers, e.g., lymphoma and skin cancer
You have a family history of hypocalcemia
You are using some drugs, e.g., proton pump inhibitors, diuretics, aminoglycosides, antiepileptic drugs, cisplatin etc.
These factors increase your risk of vitamin D deficiency and force you to go for vitamin D supplementation.
Vitamin D deficiency leaves many symptoms in adults and children. These include;
Increased incidences of bone fractures, particularly in the weight-bearing bones, e.g., bones of the hip, pelvis and legs
Brittle teeth and dental caries in children
Severe pain and weakness in the muscles and bones
Pains and aches
Tiredness
If you have these symptoms, you need to visit healthcare professionals who may ask you for a blood test to determine the vitamin D levels in the blood. A serum level of 20-40 ng/ mL is enough. A level below 20 ng/mL means deficiency. To confirm the fault, the doctor can also take an X-ray of your bones to monitor bone density.
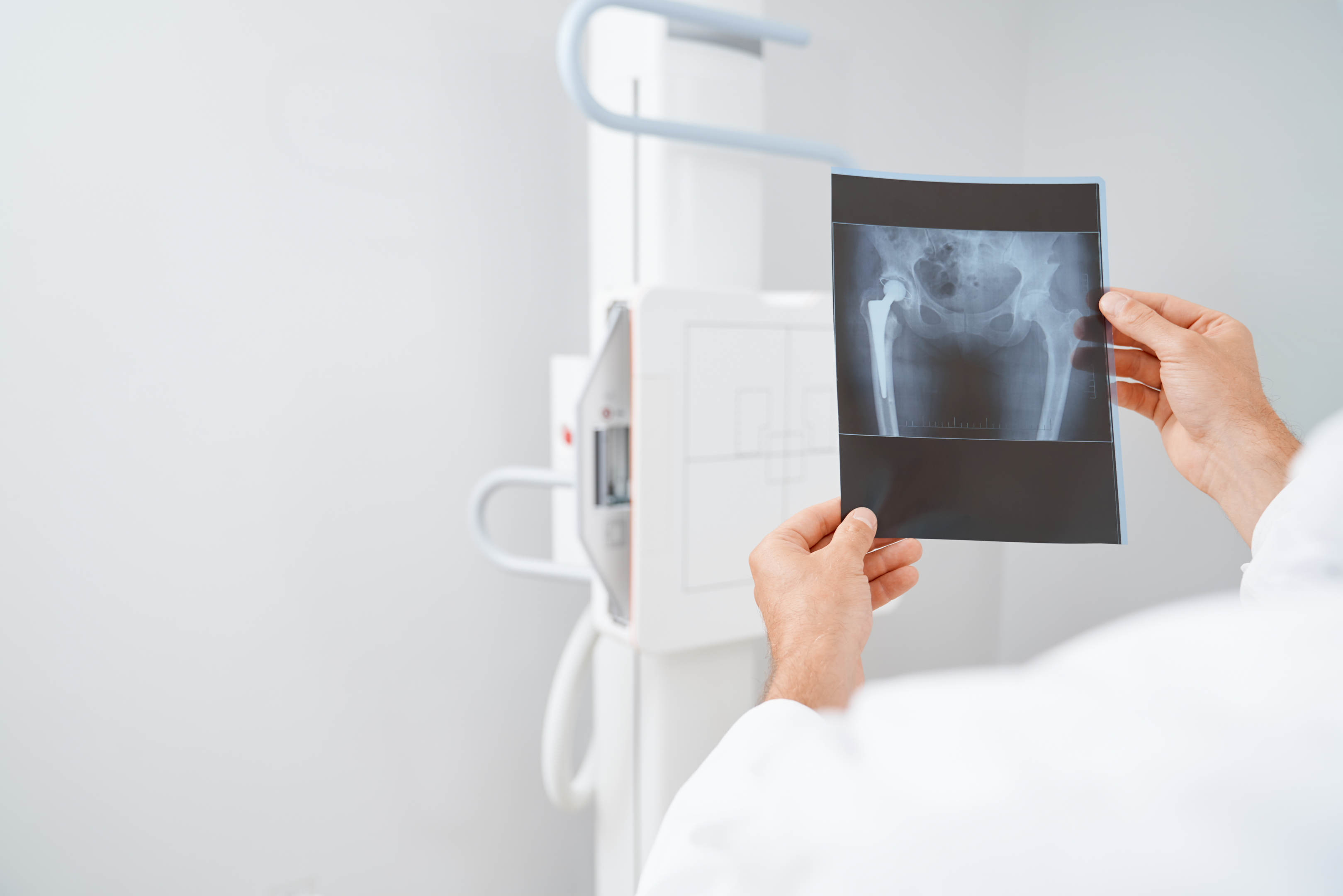
The doctor will prescribe vitamin D tablets. On your part, however, you may need to increase your exposure to sunlight.
If you have vitamin D deficiency symptoms and want to confirm them, our Vitamin D Blood Test can help you immensely. It detects vitamin D levels in your blood and provides results within 2 days. Click here to know more and place your order.
We have a similar product, the Vitamin Deficiency Test, which allows you to detect the deficiency of vitamin D, folate and vitamin B12. Click here to place your order.
So, finally, you have diagnosed your deficiency and want to go for supplementation. How much vitamin D do you need to restore your bone health?
The required dosage depends upon your age and physiological status, e.g., pregnancy. The dosage is measured in micrograms (mcg) or international units (IUs). One mcg of vitamin D has 40 IUs. The daily recommended intake for various people is;
For infants under 1 year: 10mcg (40 IU)
For children under 18 (1-18): 15mcg (600 IU)
For adults: 15mcg (600 IU)
For elderly (70 or above): 20mcg (800 IU)
For pregnant and breastfeeding women: 15mcg (600 IU).
Note: These doses are taken from the National Institute of Health guidelines. However, only the healthcare professional can prescribe the exact required dose.
The exact requirement is debatable, with some studies recommending higher intake. The daily intake should be adjusted to achieve the desired serum level of 50-100 nmol/L (nanomoles per litre) or 20-40 ng/ mL.
At Welzo.com, we have MHRA-approved Vitamin D Tablets for you. Each tablet provides 2000 IU of D3. Click here for more information and to place your order.
Remember that it is a fat-soluble vitamin, and the body will find it difficult to remove excessive vitamin D. Overdosing vitamin D will cause vitamin D toxicity. However, the good news is that the toxic dosage is several times higher than the dosage in most tablets.
The maximum permissible dosage of vitamin D is 4000 IU per day. However, according to the National Institute of Health, the toxicities are not expected at doses less than 10,000 IU/day. This limit is 5-10 times higher than the dose provided by most oral tablets.

In case of persistent higher intake, a condition develops called hypercalcemia leading to higher calcium levels in the blood, hardening of the blood vessels, heart tissue, kidney and lungs and calcification of the bones. The situation can become life-threatening and need immediate medical intervention. The common signs of hypercalcemia are;
Constipation
Diarrhoea
Dry mouth and metallic taste
Loss of appetite
Vomiting
Nausea
Headaches
For better safety, the tablets should be used after consulting the doctor as most vitamin D tablets' safety, and efficacy is questionable and not monitored by the regulatory agencies, e.g., FDA and MHRA.
Vitamin D deficiencies are rare. Nevertheless, tablets are recommended for people exposed to predisposing factors. However, some vitamin D-rich foods can also be beneficial. These foodstuffs are a good dietary vitamin D (D2) source and enhance indigenous vitamin D production. These include;
Vitamin D-fortified juices and cereals
Beef liver (a 3-ounce serving provides 42 IU of D3)
Mushrooms (variable quantities, but most mushrooms provide 1-2% of the daily requirement per 100g).
Fortified milk
Cheese (fortified cheese is a rich source of vitamin D)
Egg yolk (according to USDA, one large egg provides 5% of the daily vitamin D requirement).
Fatty fish, e.g., tuna, mackerel, salmon etc.
Herring
Fortified yoghurt

You need to resort to supplements if these foods are not providing enough vitamin D and signs of deficiency are apparent.
Many foodstuffs and drugs interfere with vitamin D metabolism. Before taking vitamin D supplements, you should be aware of these interactions, as some can be very dangerous.
Some important interactions are;
Stimulant laxatives: These laxatives stimulate the intestinal lining to facilitate bowel movements. However, their long-term use can reduce the absorption of calcium and vitamin D. So, and you may need an external source of vitamin D if you are using these drugs.
Verapamil and Diltiazem: These calcium channel blockers are common drugs used to treat high blood pressure. Their long-term use is also linked to decreased absorption of calcium and vitamin D.
Thiazide diuretics: Taking these diuretics with vitamin D supplements increases the risk of developing hypercalcemia and is therefore contraindicated with the vitamin D supplements.
Steroids: Steroids are common painkillers and anti-inflammatory compounds. However, their use is also responsible for decreased calcium absorption and impairment of vitamin D metabolism.
Drugs for cardiovascular issues and lowering blood cholesterol (e.g., atorvastatin and cholestyramine) reduce vitamin D absorption.
Anti-convulsants: Common anticoagulants, e.g., phenytoin, phenobarbital etc., reduce calcium absorption by increasing vitamin D breakdown.
Calcipotriene: It is a common drug used for psoriasis, and it also increases the risk of hypercalcemia
Vitamin D deficiencies are rare as the body can produce enough of it naturally, and they are also present in many routinely used foods. However, many lifestyles, nutritional and disease-linked factors can cause you to develop vitamin D deficiency. The deficiency leaves many noticeable signs. It can also be detected by using blood tests and X-rays. Doctors often prescribe vitamin D tablets because of the harm of vitamin D deficiency.
However, before going for tablets, you should know the pros and cons of vitamin D tablets, the required dosage, possible risks, side effects and toxicity symptoms. A regular blood calcium test to monitor serum vitamin D levels is also a good option.

Our supplements and Vitamins page has a lot of information related to vitamin supplementation. Click here to visit the page and view our products.
Welzo Health and Lifestyle Blood Test is another of our useful products which allows you to monitor various health parameters, e.g., cholesterol levels, kidney health, liver health, iron levels, inflammation, muscle health etc. Click here to place your order.
For online consultation with our health experts, click here.
Plus get the inside scoop on our latest content and updates in our monthly newsletter.